Image resolution is a confusing term that crops up repeatedly in the photo industry. Sometimes, it makes new photographers scratch their heads. Beginner photographers are often confused about DPI and PPI. Even they complain: Why is their 300dpi image blurry? What points are they missing? Why is the term image resolution so confusing?
I will explain everything in this article. This guide should help you understand it if you are a beginner. You don’t have to be confused again about image resolution.
What is Image Resolution?
The image resolution is the detail in an image. It applies to raster images, film images, and other types of digital images. The higher the resolution, the more detail an image can hold.
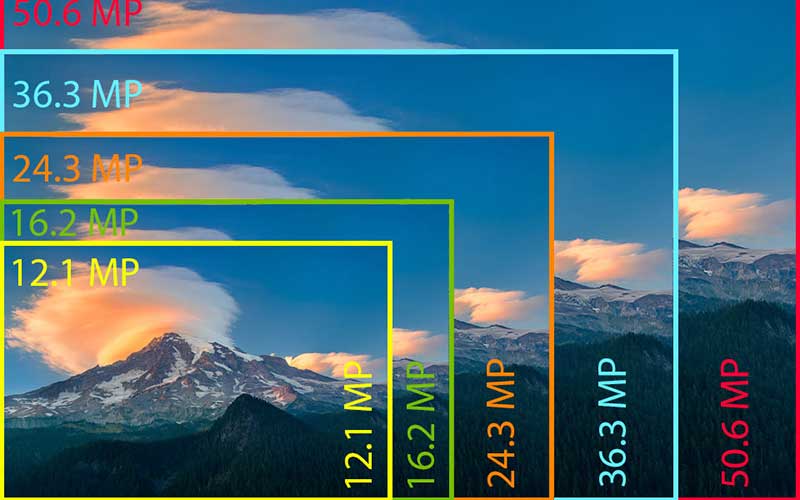
Resolution is the number of megapixels produced by an image sensor in a digital camera. This corresponds to the amount of detail a camera can capture. If your camera packs 12 MP (megapixels), it captures less detail than a camera with 24 MP. So, a camera with 40 MP can capture more detail than 24MP. But are you confused about pixels or megapixels? Let’s see what pixels are and how they affect your photos.

What are Megapixels?
Before knowing megapixels, you have to understand what a pixel is. A pixel is a physical point in a raster image or the smallest element of all points. So, the term megapixel came from the pixel. According to standard measurement, a megapixel is equal to 1,048,576 pixels. But camera & display manufacturers round this number to 1,000,000. The round figure is easier for the general public to understand.
Suppose your camera captures 16-megapixel images. It is around 16,000,000 pixels per image. But to understand pixels, it is not enough information. This only describes the total number of pixels that make up the image.
Let’s assume the dimensions of your RAW images are 4672 x 3104 pixels. To get the actual number of pixels, you need to multiply the number of pixels along the image width & height. Thus, your RAW image’s actual number of pixels will be 4672 x 3104 = 14,501,888. We may call it 14.5-megapixels. But the display or camera manufacturers round this up to 14.6-megapixels.
In other words, a pixel is a single photo element. A pixel can only be one color, and an image consists of a grid of thousands of pixels.

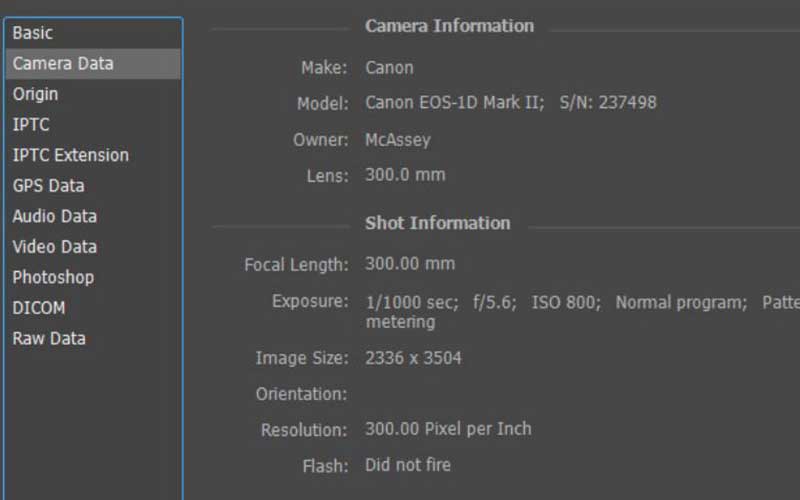
You can check camera information and image details in an image. Many image editing software contain this feature. To check camera data in Adobe Photoshop, open the image and choose File > File Info > Camera Data. This will open a dialog box that shows the image details like size, dimension, megapixels, etc.
DPI vs PPI
DPI and PPI are two important terms in image resolution. They measure the resolution or clarity of an image, but each refers to a separate media resolution, like digital vs. print.
DPI (Dot Per Inch) describes the amount of ink dots on a printed image. On the other hand, PPI (Pixels Per Inch) describes the resolution in a digital image’s pixels. PPI mainly refers to the digital display, but it also affects the print size of your design. There is nothing DPI can do digitally. Its only concern is print.
Higher PPI tends to be higher quality images with greater pixel density. If you increase the PPI, the size of your file will increase. You may want to use a high PPI only when it is needed.
Your screen’s pixel density is fixed, so PPI does not really matter for distribution on the web. A 300 PPI image and a 72 PPI image will appear the same on your display.
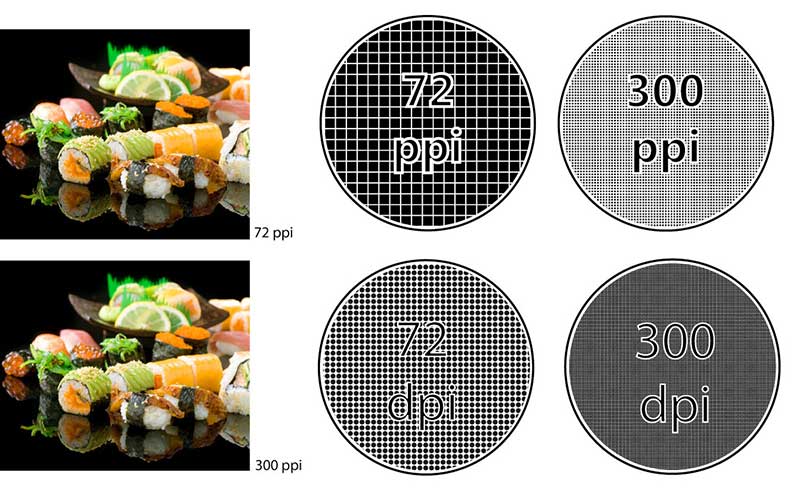
Image Size
A higher resolution means a sharper image. It would be true if all images were the same size. An image’s high or low quality depends on the relationship between pixel density and image size. If you change one, the other fact changes with it.
If you increase the image size, it will result in a lower DPI. This means there are fewer pixels to make up each square inch, so the pixels will become bigger to fill the space.
You can understand this with the flaccid balloon’s example. Keep some balloons in a small box. Then again, keep the same number of balloons in a larger box. Now, look at the two boxes carefully. What do you understand from this? You can only fill the box by inflating the balloons. The size of the balloons increases even if their number remains the same.
Resizing Images in Photoshop
You will see two different dialog boxes in Adobe Photoshop for image resolution and size. One is Image > Canvas Size, and the other is Image > Image Size. We use Canvas Size to change the ultimate size of the canvas. It never alters the image size other than to crop it. On the other hand, the Image Size box is the key to controlling the image’s resolution and dimensions.
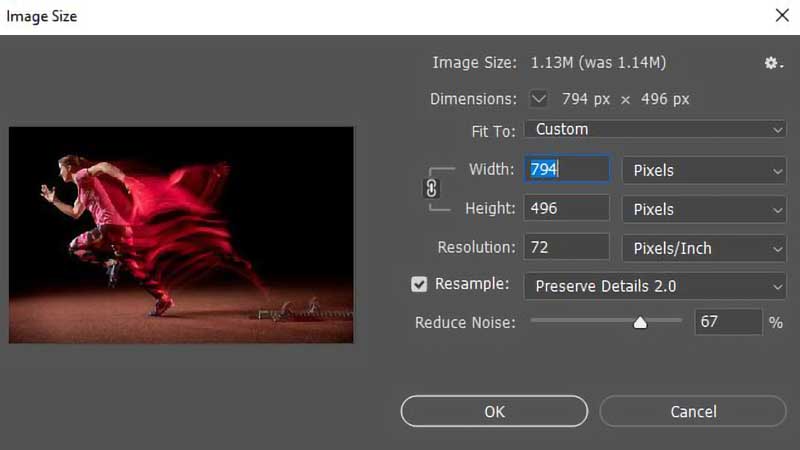
In the above image, you can see the image size box. It contains three key options for changing image size. They are Width, Height, and image Resolution. All of them are linked with each other. So, if you change one, the others will change proportionally. You can also see the file size at the top of the box, which is necessary when trying to reduce the image size. The dialog box also shows your desired resolution when you change it.
Image Resolution: Resampling
The resampling option in the dialog box allows you to change the pixel dimensions. You can do that by adding or deleting pixels. Turning on the resampling option, you can set a new resolution without changing the image size. In this case, Photoshop will fill in the missing pixels.
Conclusion
There is a myth about a megapixel that says you need more and more megapixels for great images. But it is just a marketing strategy for selling cameras. The latest cameras have over 10 megapixels nowadays, which is more than enough.
If you have enjoyed this guide, you may want to read more new content. Read about Kit Lens, Aperture, & ISO to be an expert in photography. Also, let us know if you have anything to say about image resolution.
Scientists found in experiments that the resolution of the human eye is 576 megapixels. Which is huge compare to the 12 megapixels of an iPhone camera.
The standard highest resolution is 8K Ultra HD (7680 × 4320) until now.